Table of Contents
Introduction
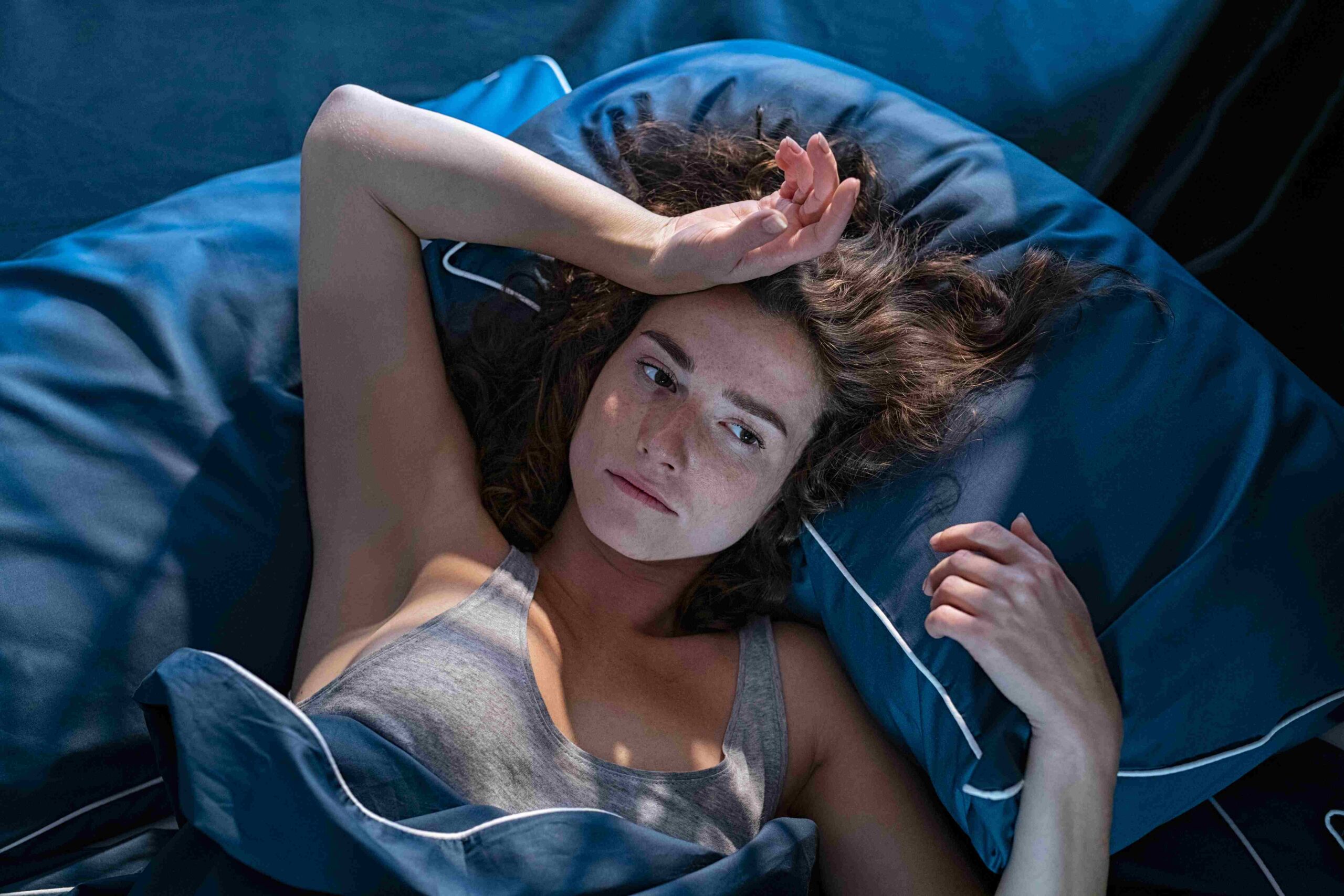
Millions of people around the world suffer from insomnia, which is a common issue. There are numerous possible reasons for this, but one that has recently attracted interest involves the function of the pineal gland in sleep control. What the Pineal Gland Does? This article will discuss the connection between pineal gland and insomnia, as well what science today thinks about how this tiny but mighty portion of the brain could affect sleep, included an affected person with insomnia.
What Is the Pineal Gland?
The pineal gland is a small, pea-sized organ deep within the brain. While small, it is responsible for regulating many biological functions such as the circadian rhythm — the sleep-wake cycle that drives our daily patterns. Many people call this gland “the third eye,” because it is light sensitive and by the visual centers of the brain.
The main purpose that this pineal gland serves is in the production of melatonin, a hormone that plays a key role in regulating your body’s circadian rhythm. Circadian rhythm — your body’s internal clock that controls when you sleep, wake and carry out other processes throughout a 24-hour day. The pineal gland releases melatonin, which is the cue for the body to sleep and thus helps you go through a natural sleep cycle.
Melatonin and Its Importance in the Sleep Process
Melatonin works mainly by regulating the circadian rhythm, thus allowing sleep. If darknesses are secreted, it sends the brain a message that it is nighttime. Light inhibits melatonin release, and therefore, sleep disruptions happen when people encounter artificial lighting during nighttime.
Melatonin levels naturally increase in the evening and peak during the night to facilitate sleep in a healthy person. But in people who struggle with insomnia, melatonin production and release can be interrupted or malfunctioning so that it takes longer to fall asleep or stay asleep. The pineal gland-insomnia connection matters most here in this disruption.
Heading The Role of the Pineal Gland and Its Effects on Sleep
The disruption of pineal gland function resulting in insomnia or any other sleep disorder can also be caused by a number of factors. These are some of those factors:
The Pineal Gland and Light.
The pineal gland reacts very quickly to light, and so the internal body clock is very closely related to light conditions in the environment. Today people at least in the developed world are surrounded by artificial light sources during night, especially light from smartphone screens or computer screens or TV where they watch a movie. The melatonin production is inhibited with this false light which makes it harder for you to go to sleep. This is particularly bad news for insomniacs whose pineal glands might not secrete the right amount of melatonin, or who simply secret it too late as a result of light exposure.
The Pineal Gland: What Happens as You Age
With age, the function of the pineal gland tends to decline. As people get older, they tend to create less melatonin, which can lead to doses of slumber. One of the factors contributing to older adults being more susceptible to insomnia and other sleep disorders is reduced melatonin levels. Although part of this is simply aging, the effect these changes have on a person and their relationship with sleep can be profound.
Stress and the Pineal Gland
Furthermore, excessive stress will disrupt the pineal gland. Stress also elevates the secretion of cortisol—a hormone that is closely linked with the fight-or-flight mechanism. Increased levels of cortisol can inhibit melatonin and compromise the ability to sleep. This can be a problem for those who have insomnia as stress and anxiety could easily worsen the sleeping problems.
The Science Behind Pineal Gland and Insomnia: What It Means?
Studies have now confirmed the role of this gland in our body for regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Research has shown that people with insomnia are more likely to have irregular melatonin production and circadian rhythms. In actuality, studies indicate melatonin acts as a sleep aid in insomnia patients.
In fact, another study published in the Journal of Pineal Research indicated that melatonin supplementation helps normalize sleep in patients with disrupted circadian rhythms. Based on the outcome of their study, they suggested melatonin may be utilized as a treatment for patients suffering from insomnia, especially in cases where sleep disruption relates to impaired functioning of the pineal gland.
Meanwhile, a separate study appearing in the peer-reviewed journal Sleep Medicine Reviews associated disorders of circadian rhythms with insomnia. Image caption, Difficulty regulating melatonin could explain why insomnia sufferers struggle with maintaining a consistent hypnogram And this also highlights the role of sleep and the pineal gland in managing that.”
Cure for Insomnia Caused from Pineal Gland Disorder
Since the pineal gland plays a significant role in the regulation of sleep, various treatments have been proposed for sleepless people. These interventions are frequently designed to restore appropriate melatonin levels and reestablish the body’s circadian rhythms. The following are some of the most frequently used treatments:
Melatonin Supplements
Melatonin supplements are commonly prescribed for insomnia, especially when it is tied to misaligned circadian rhythms. Such supplements are normally advised for people who are not producing sufficient melatonin because of their pineal glands. Taken in supplemental form, melatonin can help people “reset” their internal clock to sleep better and on a more regular schedule.
Nevertheless, it is necessary to seek advice from a healthcare professional to take melatonin supplements as improper use may cause side effects and dependence.
Light Therapy
It is another good option for treating insomnia associated with dysfunction of the pineal gland. This involves exposure to bright light during certain times of the day in order to regulate a circadian rhythm. Light therapy helps especially those with sleeping problems that stem from an internal clock (circadian rhythms) not matching up to the external world.
Melatonin is often used together with light therapy to help you sleep better and longer.
Lifestyle Modifications
For those with insomnia, implementing lifestyle changes that promote better sleep can also ease their condition. These changes may include:
- Setting a regular sleep schedule
- Lowering the use of alcohol and caffeine, particularly during the evening
- Establishing a wind down routine before sleep
- Limit screen time before sleeping to reduce light exposure
Sufficient Sleep Hygiene Matters
Apart from medication and supplements, sleep hygiene is an important cornerstone for insomnia treatment. Good sleep hygiene is creating a space that allows for a great nights rest. This includes:
- Making the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet
- Buying a nice mattress and pillows
- Reducing noise and distractions.
- Using relaxation techniques before bed such as deep breathing or meditation
Such methods could help alleviate sleep problems associated with this gland, and by adding them to the daily routine, people suffering from insomnia may be able to manage sleeping better.
Conclusion
The relationship between the pineal gland, insomnia and light is truly complex and has huge significance. Disturbance to the function of the pineal gland, including its secretion of melatonin may cause sleep problems and insomnia. There is scientific research on the role of melatonin supplementation, light therapy, and lifestyle changes in normalizing sleep patterns for insomniacs.
By studying the pineal gland and its involvement in sleep, researchers can deploy effective treatments for insomnia and ensure people lead healthy lives with proper sleep. If you are experiencing sleep problems, see a health care provider to determine the reasons for your difficulties and what treatment is appropriate.
Here are more resources, if you would like to learn about sleep disorders and their treatments